|
|
||
|
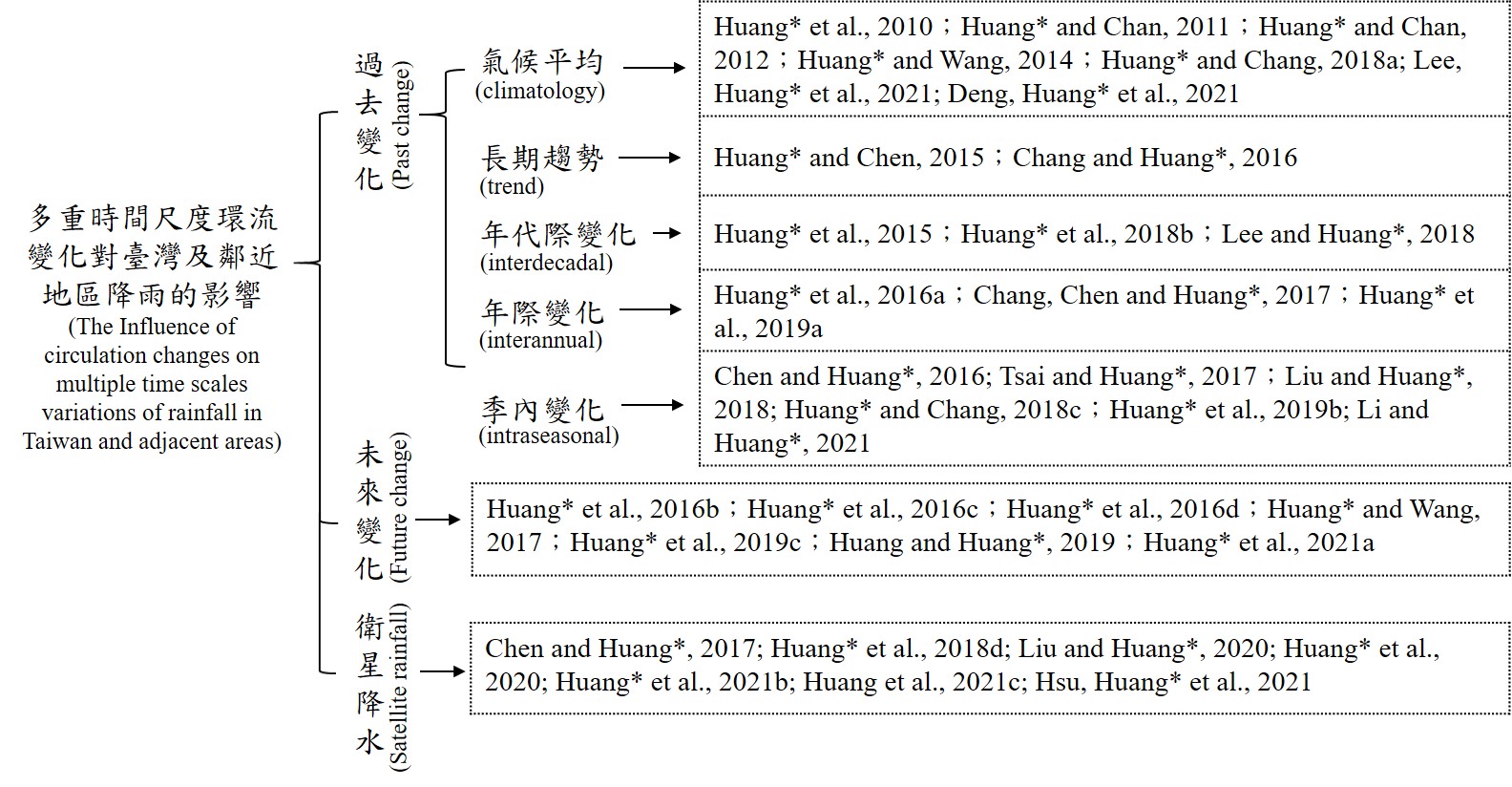
�@�B��s���G²�� ������Ǧh�~�ӭP�O�Q�u����ܾE�U�O�W�P�F��a�Ϫ������S���ܤƤά�������v(Table1)�C�S�O�O�w���u�j�ث����y�������ܾE��O�W�P�ثn�a�Ϥ�]�ܤƭ����ƥ�(diurnal rainfall events; �p�ȫ��y)���v�T�v�o��ij�D���@�t�C�����R�Φ��G�A��s���e�]�A�[�� (�t�ìP�[���δ����[��) ��ƤμҦ�����(�t���y�Ҧ��ΰϰ�Ҧ�)��ƪ����R�A���R���ɶ��ثץ]�A:��ԥ������B�����ͶաB�~�N���ܤơB�~���ܤ��B�u���_���ܤơA�H�Υ��Ӯ���ܾE�U�������C �z�L�h���[����ƪ����R��ڭ̵o�{�G(1) �O�W����]�ܤƭ����ƥ�A��ɶ��������ϰ�ʮt���A�B���t���P�u�j�ثP�ϰ�ثפ�]���y�������椬�@�Ρv�����]Huang and Wang, 2014; Huang and Chang, 2018a�^�C(2) �O�W�P�ثn�a�ϱ��B�u���W�������Τȫ��y�����Ҧs�b�۪����Ͷ��ܤơA�B���Ͷ��ܤƩM�j�����y���O�B�ʤO�L�{�������ܾE�����]Huang and Chen, 2015a; Chang and Huang*, 2016�^�C(3)�u�O�W�a�Ϥȫ��y�����������Ͷաv�s�b����۪��ϰ�ʮt���A�B���t����O����j�ث����y�ܾE���v�T�]Huang et al., 2015b�^�C(4)�O�W�a�Ϥȫ��y�������o���W�v�έ��B�j�|����j�ث����y�u���_���{�H�]Huang and Chang, 2018b�^�A�F�ӥ��v�������~���ܤ��v�T (Huang et al., 2019a)�Φ~�N���ܤƼv�T (Huang et al., 2018c)�C ���~�A�z�L�h��CMIP5�B6�]Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5�BPhase 6�^��ԼҦ���Ƥ��R�B�ϰ�Ҧ����ث�Ƥ��R�A�ڭ��˵��F���P�Ҧ���F��(�t�O�W)�a�ϥ��ӭ����ܤƤ��������G�C�ڭ̪���s�o�{�G(1) 18 ��CMIP5�Ҧ����HCMCC-CM�Ҧ��̯�x���F�Ȧa�ϱ��B�u��]�ܤƭ������ɪŤ������p�C���Ҧ��������ӻO�W�P�ثn�a�Ϩ���u��F���Ǽ��S�ʪ������t�μv�T�v�����|�N�ܦh�]Huang and Wang, 2017�^�C(2) �N���y�Ҧ���Ƴz�LWRF�Ҧ��i��ʤO���ث᪺���G�A��ħﵽ�Ҧ����x�O�W�L�u��]�ܤƭ����ƥɡB�Ť����S���]Huang
et al., 2016a�^�A�B����k��A�Ω�ﵽ�Ҧ����x�ثn�P�f���a�ϮL�u��]�������ɡB�ůS�ʤ����]Huang
et al., 2016b�^�C(3) �ϰ�Ҧ����ثױ������Ӧ]����j�ث���ܾE���v�T�A�U�����������]�t�ȫ��y�B�W���B�䭷�Ψ�L�n�Ӫ������t�Ρ^��O�W�L�u�����q���^�m�N���Ҥ��P�]Huang
et al., 2016c�^�A�䤤�ȫ��y���W�v�N���{�b�֡C(4) �̷s�@�N��CMIP6�Ҧ����A�HEC-Earth3 �t�C���~��O�W�B�ثn�Χf���ȫ��y���B�ƥ��W�v�B�j�ת��{���̦n�C�j������CMIP6�Ҧ����w�����ӻO�W���ȫ��y���B�ƥ��W�v��֡B�j�W�j���{�H�C���M�j�𪺰ʤO�B���O�����ܤƦ��� (Huang et al. 2021a)�C ��ӡA�ڭ̥�w��O�W�����ݭ����ܤƦb�L�h(Huang et al., 2019b) �Υ���(Huang et al., 2019c)���i��|�p�����j�ث����y�ܤƶi�������s�C�åB�ڭ̧Q��CESM2-LE��CMIP6�Ҧ����Q�F�O�W���B�u���B����{�H���i�ॼ���ܾE(Huang et al., 2022a)�C�t�@�譱�A�ڭ̰w��u�s�@�N�ìP��ƹ�O�W�����S�⪺���{��O�����P���Ρv���@�t�C�������G�o��(Huang et al., 2018d;
Huang et al., 2020; Liu and Huang, 2020; Huang et al., 2021b,c,d;
Hsu et al., 2021a,b)�C���~�A�ڭ̥�ϥ�MODIS�ìP�[����Ʒf�t�a���[����ƶi����R�A�F�Ѥ��n�b�q�K�u�ͽ�U�N��O�W���L�s�[���쪺PM10���~���ܤƤ��i��v�T�A�ñq���y�B���������ܤƴ��Ѭ����ʤO�B���O���� (Huang et al., 2016d)�C�t�@�譱�A�ڭ̤]�ϥνìP������f���L�u���y���B���L�h�ܾE�S��Φ��]�i����R(Huang et al., 2022b)�C�o�Ǭ�s���G�Ҧ��U��ڭ̤F�ѻO�W�P�F��a�Ϫ��������i��|�p��������ܾE���v�T�C My academic expertise is
in climate data analysis and dynamic mechanism examination of global and
regional precipitation changes. Most of my research has focused
on exploring how climate change affects precipitation changes in Taiwan
(Table 1). In particular, I have conducted a series
of studies to prove that the local afternoon rainfall events in Taiwan are
affected by large-scale circulation changes on multiple timescales. The time
scales covered by my research topics include: climatology, long-term trend,
interdecadal variation, interannual variation, intraseasonal variation, and
future projection. The major achievement of this research group is to
successfully investigate the characteristics and maintenance mechanisms of
afternoon rainfall activities in Taiwan from a new perspective of changes in
multiple timescales. For a long time, the afternoon rainfall convection in
Taiwan has been regarded as a local event mainly modulated by changes in the
local diurnal circulation. However, our research works show that the
activities (frequency and intensity) of afternoon convective rainfall in
Taiwan include long-term trend, interdecadal, interannual, and intraseasonal
changes. These changes are not only regulated by changes in local
circulation, but also by changes in large-scale circulation. In addition,
through the application of global climate model data, our research works have
demonstrated the possible impact of future atmospheric circulation changes on
precipitation in Taiwan. These findings are very important for understanding
how the precipitation in Taiwan can be affected by global climate changes. Recently,
we have also expanded research interests to prove the ability of new
satellite precipitation observations applied for research uses in Taiwan.
Table
1:
����s�ǥD�ɪ���sij�D�ξ�CSummary of the work led
by this research group. �����s²���G �P
MJO�������d�K��u�`���y�����ƥv�T (Huang et al., 2024; npj Clim Atmos Sci) �P
���y�x�ƤU�A�����ܤƹ�O�W���Ӥȫ��y���ʯS�x���v�T (Huang et al., 2023; npj Clim Atmos Sci) �P
2022 �~ 1-2 ��O�W���ݭ����S�x�Φ��] (Huang et al., 2022; Weather and Climate Extremes) �P
�ثn�M�O�W��L�����S�x�����ӱ��� (Huang et al., 2022; JGR-Atmos.) �P
CMIP6 �Ҧ���F�n�ȮL�u�ȫ��y���B���ʪ������P���� (Huang et al., 2021; Journal of
Climate) �P
�p��Ħa�Q��SPEI���ƺʴ��u���B�ֳt�o�i������P����ƥ� (Li and
Huang, 2021; Sci. Total Environ.) �P
�h�ìP����[���f���q�L�u�ީ]�����������ܤ� (Huang et al., 2021; Int. J.
Appl. Earth Obs.) �P
���y�����ìP�[����ƪ��ϰ�ʮt���G�f���q���o�{ (Lee and Huang, 2023; Earth and Space Science) �P
�h�ث����y�椬�@�ι�f���q�K�u�魰�����v�T (Lee et al., 2021; Scientific
Reports) |
|||
|
�G�B�a�A�ƶ� Ø �ե~ 1. ����d�j�ߥ��ͬ����� (2018) 2. ���إ���a�y��ǾǷ|�j�D�s�H�� (2017) 3. ����u�q�~���Ǫ̭p�e (2017) 4.
����ɧU�j�M�հ|���y�S���u�q�H�~ (2016-2024) 5. �a�y��Ƕ��Z (Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Journal) 2017-2018 �u�}�f�d�H�� 6. ���إ���j���Ǵ��Z�u�}�פ�� (2018�B2020) 7. ���l�⩤�C�~�j���ǾdzN��Q�|�̨νפ�� (2016) 8. �ѻP���פ�Wang et al.
(2015) ������CBS News���� Ø �դ� 1.
��O�W�v�d�j�ǯS�u�б� (2019-2021) 2.
��O�W�v�d�j���u�u�б� (2014-2018) 3.
��O�W�v�d�j��107�~��s�Z�u�� (2019) 4.
��O�W�v�d�j��111�~�ױо��u�}�� (2022) �T�B�dzN�A�� 1. ��F�|�����a�`���Ϸ|���e�� (2023/8-2025/7) 2. ��F�|�a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe���|�ĤQ�G���e�� (��x���l���H) (2025-2026) 3. ��F�|�a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe���|�ĤQ�@���e�� (��x���l���H) (2023-2024) 4. ��F�|�a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe���|�ĤQ���e�� (��x��) (2021-2022) 5. ���F���D�ޤ����a�`���Ϸ~�ȭp�e�˰Q��i�M�ױ��ʱ��ʤp��(���a��)�e�� (2021-2023) 6. �s�_���ĤK���a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe�� (2025-2026) 7. �s�_���ĤC���a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe�� (2023-2024) 8. �s�_���Ĥ����a�`���ϱM�a�Ըߩe�� (2021-2022) 9. ����j���ǾǪ����f�e��(2021-2023) 10. ������a�Ǫ���H�����f�e��(2018-2020) 11. ���إ����H�Ƿ|�j���Ǵ��Z�D�s (2021-2025) 10. Associate guest editor of TAO special issue: Taiwan-Philippine VOTE-Meteorology: Typhoon study and
related natural hazard (2021) �|�B
�dzN�ۧ@ (*�q�T�@�̡F +��s�Ǧ���) 1.
Huang, W.-R.*, Hai Bui-Manh+, T.-Y. Chiang+, and S. B. Koralegedara+, 2025:
Seasonal Variations of Diurnal Rainfall Characteristics over Vietnam. Science of
The Total Environment, 971, 179058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2025.179058 2.
Huang, W.-R.*, S. B. Koralegedara+, T.-Y.
Chiang+, C.‑A. Lee+, P.-H. Tung+, Y.-T.
Chien+, and L. Deng, 2024: The Impact of the Madden-Julian
Oscillation on Spring and Autumn Diurnal Convection in Sri Lanka. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science. 7,
42. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-024-00586-5 (IF: 9.0) Nature �l���Z 3.
Huang, W.-R.*, Y.-T. Chien+, C.-T. Cheng, H.-H. Hsu, and S. B. Koralegedara+, 2023: The Role of Sea Surface
Temperature in Shaping the Characteristics of Future Convective Afternoon
Rainfall in Taiwan. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science. 6,
198. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-023-00528-7 (IF: 9.0) Nature �l���Z 4.
Lee,
C.-A.+ and W.-R.
Huang*, 2023. Advantages of GSMaP data for
multi-timescale precipitation estimation in Luzon. Earth and Space Science, 10, e2023EA002980. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023EA002980 (IF: 3.68) 5.
Koralegedara, S.B.+, W.-R.
Huang*, P.-H. Tung+ and T.-Y. Chiang+, 2023. El
Niño-Southern Oscillation modulation of springtime diurnal rainfall over a
tropical Indian Ocean island. Earth and Space Science, 10, e2023EA002832. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023EA002832 (IF: 3.68) 6.
Huang, W.-R.*, S. B. Koralegedara+, P.-H. Tung+
and T.-Y. Chiang+, 2023: Seasonal changes in diurnal rainfall over
Sri Lanka and possible mechanisms. Atmospheric
Research, 286, 106692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2023.106692 (IF: 5.965) 7.
Huang,
S.-C., W.-R. Huang*, Y.-C.
Wu, Y.-C. Yu, J.-L. Chu, and B. J.-D. Jou, 2022:
Characteristics and causes of Taiwan's extreme rainfall in 2022 January and
February. Weather and Climate Extremes.
100532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2022.100532 (IF: 7.761) 8.
Hsu,
J.+, W.-R.
Huang*, and P.-Y. Liu+, 2022: Comprehensive analysis of
PERSIANN products in studying the precipitation variations over Luzon, Remote
Sens. 14, 5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225900 (IF: 5.349) 9.
Huang, W-R*,
P.-Y. Liu+, S.-Y. Lee, and C.-H. Wu, 2022a: Changes
in early summer precipitation characteristics over South China and Taiwan:
CESM2-LE and CMIP6 multi-model simulations and projections. Journal of
Geophysical Research �V Atmospheres. 127, e2022JD037181. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022JD037181 (IF: 5.217) 10. Huang, W.-R.*,
J. Hsu+, P.-Y. Liu+, and L. Deng,
2022b: Multiple satellite-observed long-term changes in the summer diurnal
precipitation over Luzon and its adjacent seas during 2000�V2019. International
Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 110, 102816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2022.102816 (IF: 7.672) 11. Wu,
C.-H.*,
P.-C. Tsai, W.-R. Huang,
and S.-Y. Simon Wang, 2022: Winter�Vsummer contrast of the 1990s decadal
change in relation to Afro�VAsian monsoons.
Climate Dynamics. 59,
1969�V1980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06191-7 (IF: 4.901) 12. Huang S.-H., P.-Y. Lai, S.-Y. Hwang*, Krishna Borhara,
W.-R. Huang, and S.-Y. Wang, 2022: Climate Variability Shifting
Immigrated Rice Planthoppers in Taiwan. Climate,
10, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10050071 13. Chien, F.-C.*, W.-R. Huang,
and B. J.-D. Jou, 2021: Introduction to the special
issue on Taiwan-Philippine VOTE-Meteorology: Typhoon Study and Related
Natural Hazard. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci.,
32, 613-617. DOI: 10.3319/TAO.2021.10.13.01 (IF: 0.963) 14.
Huang, W.-R.*, Y.-H. Chang+, L. Deng, and P.-Y. Liu+, 2021a:
Simulation and Projection of Summer Convective Afternoon Rainfall Activities
over Southeast Asia in CMIP6 Models. Journal
of Climate, 34,
5001�V5016. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0788.1 (IF: 5.38) 15. Hsu, J.+, W.-R. Huang*, and P.-Y. Liu+, 2021a:
Performance assessment of GPM-based near-real-time satellite products in
depicting diurnal precipitation variation over Taiwan. Journal of Hydrology: regional studies, 38, 100957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100957 (IF: 5.437) 16. Li, X. and W.-R. Huang*, 2021: How long should the pre-existing
climatic water balance be considered when capturing short-term wetness and
dryness over China by using SPEI? Science
of the Total Environment, 786, 147575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147575 (IF:
10.754) 17.
Huang, W.-R.*, P.-Y. Liu+, and J. Hsu+, 2021b: Multiple
timescale assessment of wet season precipitation estimation over Taiwan using
the PERSIANN family products.
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,
103, 102521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102521 (IF: 7.672) 18. Lo, S.-H., C.-T. Chen*, S. Russo; W.-R. Huang, M.-F. Shih, 2021:
Tracking Heatwave Extremes from an Event Perspective. Weather and Climate Extremes, 34, 100371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2021.100371 (IF: 7.761) 19. Lee, C.-A. +, W.-R. Huang*, Y.-H.
Chang+, and S.-M. Huang, 2021: Impact of multiple-scale circulation interactions on the spring diurnal
precipitation over Luzon. Scientific Reports. 11, 9937. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89392-0 (IF: 4.6) Nature �l���Z 20.
Huang, W.-R.*, P.-Y. Liu+, J. Hsu+, X. Li, L. Deng, 2021c:
Assessment of near-real-time satellite precipitation products from GSMaP in monitoring rainfall variations over Taiwan. Remote Sensing, 13, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020202 (IF: 5.349) 21. Huang, W.-R.*,
P.Y. Liu+,
Y.H. Chang+, and C.A. Lee+, 2021d: Evaluation
of IMERG Level-3 Products in Depicting the July to October Rainfall over
Taiwan: Typhoon Versus Non-Typhoon. Remote
Sensing,
13, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040622 (IF: 5.349) 22.
Hsu, J. +, W.-R. Huang*, P.-Y. Liu+, and X. Li, 2021b: Validation of CHIRPS
precipitation estimates over Taiwan at multiple timescales. Remote Sensing, 13, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020254 (IF: 5.349) 23. Deng, L., W.-R. Huang*, J. Chen, and S.-Y. Wang, 2021:
Dissipation process of summer tropical easterly waves in Western North
Pacific. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans, 93, 101208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2021.101208 (IF: 2.049) 24.
Huang, W.-R.*, P.-Y. Liu+,
Y.-H. Chang+ and C.-Y. Liu, 2020: Evaluation
and Application of Satellite Precipitation Products in Studying the Summer
Precipitation Variations over Taiwan. Remote Sensing, 12,
347. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030347 (SCI) 25.
P.-Y. Liu+ and W.-R. Huang*, 2020: Comparison of the Warm Season Rainfall
Estimations in Taiwan during 2014-2017 from IMERG Version 5 Early, Late, and
Final run Satellite Products. Journal
of Geographical Science. 96, 1-26. (in
Chinese with an English abstract)
https://www.geog.ntu.edu.tw/images/journal/journal78_100/G96-01.pdf (TSSCI) 26.
Li X.*, Z. Wen, and W.-R. Huang, 2020: Modulation of South
Asian Jet wave train on the extreme winter precipitation over Southeast
China: Comparison between 2015/16 and 2018/19. J. Climate, 33,
4065-4081. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0678.1 (SCI) 27.
Ye, C., L. Deng*, W.-R. Huang, and J. Chen, 2020: Comparison of the
Madden�VJulian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South
China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern
Oscillation Conditions. Atmosphere,
11, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020183 (SCI) 28.
Liu
C.-Y.*, P. Aryastana, G.-R. Liu and W.-R. Huang, 2020: Assessment of Satellite Precipitation Product
Estimates over Bali Island. Atmospheric
Research, 244, 105032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105032 (SCI) 29.
Huang, W.-R.*, Y.-H. Chang+ and P.-H. Huang+, 2019a:
Relationship between the Interannual Variations of Summer Convective
Afternoon Rainfall Activity in Taiwan and SSTA(Niño3.4) during 1961-2012:
Characteristics and Mechanisms. Scientific Reports, 9, 9378. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-45901-w (SCI) Nature �l���Z 30.
Huang, W.-R*, P.-Y. Liu+,
J.-H. Chen and L. Deng, 2019b: Impact of Boreal Summer Intraseasonal
Oscillations on the Heavy Rainfall Events in Taiwan during the 2017 Meiyu season. Atmosphere, 10, 205. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/10/4/205 (SCI) 31.
Huang, W.-R.*, P.-H. Huang+, Y.-H.
Chang+, C.-T. Cheng, H.-H. Hsu, C.-Y. Tu and A. Kitoh
2019c: Dynamical Downscaling Simulation and Future Projection of Extreme
Precipitation Activities in Taiwan during the Mei-Yu Seasons. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 97, 481-499.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jmsj/97/2/97_2019-028/_article (SCI) 32.
Wu, Y.-C.*, S.-Y. Wang, Y.-C. Yu, C.-Y.
Kung, A.-H. Wang, S. A. Los., W.-R.
Huang, 2019: Climatology and Change of Extreme Precipitation Events
in Taiwan Based on Weather Types. International Journal of Climatology,
39, 5351-5366. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.6159 (SCI) 33.
Huang, P.-H. + and W.-R. Huang*, 2019:
Projections of Extreme Rainfall in Taiwan during the Mei-Yu Season based on
Multiple Sea Surface Temperature Changes. Journal of Taiwan
Water Conservancy, 67, 1-11. (in Chinese with an English abstract) (EI) 34.
Lee, C.-A. + and W.-R. Huang*, 2019: Changes in Low-Frequency Variations of
Autumn Rainfall in Taiwan. Atmospheric Sciences, 46, 317-337. (in Chinese with an English abstract) http://mopl.as.ntu.edu.tw/web/ASJ/46/46-3-4.pdf ���إ���j���Ǵ��Z�u�}�פ�� 35.
Huang, W.-R.* and Y.-H.
Chang+, 2018a: Characteristics and Mechanisms of the Diurnal
Variation of Winter Precipitation in Taiwan. International Journal of Climatology, 38, 3058-3068. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.5482 (SCI) 36.
Huang, W.-R.* and Y.-H. Chang+,
2018b: Impact of Boreal Summer Intraseasonal
Oscillations on Warm Season Diurnal Convection Activity in Taiwan. International Journal of Climatology, 38,
2187-2200. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.5326. (SCI) 37.
Huang, W.-R.*, S.-Y. Wang and B.-T. Guan, 2018c: Decadal fluctuations in the western Pacific recorded by long
precipitation records in Taiwan, Climate
Dynamics, 50, 1597�V1608. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-017-3707-9 (SCI) 38.
Huang, W.-R.*, Y.-H. Chang+
and P.-Y. Liu+, 2018d: Assessment of IMERG precipitation over
Taiwan at multiple timescales. Atmospheric Research, 214, 239-249. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809518304666 (SCI) 39.
Wu, C.-H.*, W.-R.
Huang, S.-Y. Simon Wang, 2018: Role of Indochina Peninsula Topography
in Precipitation Seasonality over East Asia. Atmosphere, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9070255 (SCI) 40.
Liu, P.-Y. +, W.-R. Huang*, Y.-H. Chang+,
P.-H. Huang+, and J.-H. Chen, 2018:
Evaluation of CWB/GFS in Forecasting the Characteristics of Mei-yu Season Rainfall over Taiwan at Different Phases of
Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillations: Using 2016-2017 as Examples. Atmospheric
Sciences,46, 372-403. http://mopl.as.ntu.edu.tw/web/ASJ/46/46-4-2.pdf (in Chinese with an English abstract) 41.
Huang, W.-R* and S.-Y. Wang, 2017: Future Changes in Propagating and
Non-propagating Diurnal Rainfall over East Asia, Climate Dynamics, 49, 375�V389. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-016-3348-4 (SCI) 42.
Chang Y.-H. +,
K.-C. Chen+ and W.-R.
Huang*, 2017: Application and Improvement of Physical-Empirical Model
on the Prediction of Interannual Variation of Meiyu
Season Rainfall in Taiwan. Atmospheric Sciences, 45, 333-348. (in Chinese with an English abstract) 43.
Tsai, M.-Y. +
and W.-R. Huang*, 2017: Impact of 30~60 day
Intra-seasonal Oscillation on the Characteristics of Summer Rainfall in
Taiwan. Atmospheric Sciences, 45,
241-261. (in Chinese with an English abstract) 44.
Chen, S.-Y. +
and W.-R. Huang*, 2017:
Evaluation on the Performance of TRMM, CMORPH, and PERSIANN in Depicting the
Diurnal Precipitation Variation in Taiwan. Atmospheric Sciences, 45, 167-191.(in Chinese with an English abstract) 45.
Huang, W.-R.*,
Y.-H. Chang+, C.-T. Cheng, H.-H.
Hsu, C.-Y. Tu and A. Kitoh, 2016a: Summer
Convective Afternoon Rainfall Simulation and Projection using WRF Driven by
Global Climate Model. Part I: over Taiwan. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (TAO), 27, 659-671. http://tao.cgu.org.tw/index.php/articles/archive/hydrology/item/1470-2016050201tccip (SCI) ���إ���a�y��ǾǷ| 2017�j�D�s�H�� 46.
Huang, W.-R.*,
Y.-H. Chang+, H.-H. Hsu, C.-T. Cheng, and C.-Y.
Tu, 2016b: Summer Convective Afternoon Rainfall Simulation and
Projection using WRF Driven by Global Climate Model. Part II: over South
China and Luzon. Terrestrial,
Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (TAO), 27, 673-685. http://tao.cgu.org.tw/index.php/articles/archive/hydrology/item/1471 (SCI) 47.
Huang,
W.-R.*, Y.-H.
Chang+, H.-H.
Hsu, C.-T. Cheng, and C.-Y. Tu, 2016c: Dynamical Downscaling
Simulation and Future Projection of Summer Rainfall in Taiwan: Contributions
from Different Types of Rain Events. J. Geophys.
Res. Atmos. 121, 13973-13988. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2016JD025643 (SCI) 48.
Huang, W.-R.*, S.-H. Wang, M.-C. Yen,
N.-H. Lin, and Parichart Promchote,
2016d: Interannual Variation of Springtime
Biomass Burning in Indochina: Regional Differences, Associated Atmospheric
Dynamical Changes, and Downwind Impacts.
J. Geophys.
Res. Atmos., 121, 10016-10028. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2016JD025286 (SCI) 49.
Chang, Y.-H. + and W.-R. Huang*,
2016: Convective Afternoon Rainfall Activities in Taiwan during the 2016 Meiyu Season. Atmospheric Sciences. 44, 289-304 (in
Chinese with an English abstract) ���إ���j���Ǵ��Z�u�}�פ�� 50.
Chen, K.-C. + and W.-R. Huang*,
2016: Evaluation of CWB Global Forecast System in Forecasting the
Precipitation over East Asia during 2016 May and June. Atmospheric Sciences. 44, 305-236 (in Chinese with an English
abstract) 51.
Li, Y., C. Y. Tam, W.-R. Huang, K. K. Cheung, and Z. Gao, 2016: Evaluating the impacts of cumulus, land surface and ocean surface
schemes on summertime rainfall simulations over East-to-southeast Asia and
the western north Pacific by RegCM4. Climate
Dynamics, 46, 2487-2505. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-015-2714-y (SCI) 52.
Huang, W.-R.* and K.-C. Chen+, 2015a: Trends in Pre-Summer
Frontal and Diurnal Rainfall Activities during 1982-2012 over Taiwan and
Southeast China: Characteristics and Possible Causes. International
Journal of Climatology, 35: 2608�V2619. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.4159 (SCI)�ꤺ�C����� 53.
Huang, W.-R.*, H.-H.
Hsu, S.-Y. Wang, and J.-P. Chen+, 2015b: Impact of atmospheric changes on the low-frequency
variations of convective afternoon rainfall activity over Taiwan, J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 120, 8743�V8758. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2015JD023568
(SCI)���l�⩤�C�~�j���ǾdzN��Q�|�̨νפ�� 54.
Wang, S.-Y. S., W.-R. Huang, H.-H. Hsu, and R.
Gillies, 2015: Role of the strengthened El Niño
teleconnection in the May 2015 floods over the southern Great Plains, Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 8140-8146. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2015GL065211 (SCI)�����iCBS News�j���� 55.
Wang, S.-Y. S., W.-R. Huang
and Yoon, J.-H., 2015: The North American winter ��dipole�� and extremes
activity: a CMIP5 assessment. Atmosph. Sci. Lett.,
16: 338�V345. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asl2.565 (SCI) 56.
Chang, F.-R. +, W.-R. Huang* and C.-C.
Wang, 2015: The Effects of Long-Term Climate Change on Eastward
Propagating Rainfall Events over the Yangtze River Valley: Example of May
2009. Atmospheric Sciences, 43,
265-284. (in Chinese with an English abstract) 57.
Huang, W.-R.* and S.-Y.
Wang, 2014a: Impact of Land-Sea Breezes at Different Scales on the Diurnal
Rainfall in Taiwan. Climate Dynamics, 43, 1951�V1963. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-013-2018-z (SCI) 58.
Huang, W.-R.* and Johnny
C. L. Chan, 2014b: Dynamical Downscaling Forecasts of Western North Pacific
Tropical Cyclone Genesis and Landfall. Climate
Dynamics, 42, 2227�V2237. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-013-1747-3 (SCI) 59.
Huang, W.-R.*, Johnny C.
L. Chan and Andie Y. M. Au-Yeung, 2013: Regional Climate Simulations of Summer
Diurnal Rainfall Variations over East Asia and
Southeast China. Climate
Dynamics, 40:1625�V1642 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-012-1457-2 (SCI) 60.
Huang, W.-R.*, T.-C. Chen and
S.-Y. Wang, 2012: Co-variability
of poleward propagating atmospheric energy with tropical and higher-latitude
climate oscillations, Climate Dynamics, 39, 1905-1912 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1238-3 (SCI) 61.
Huang, W.-R.* and Johnny C. L. Chan, 2012: Seasonal
variation of diurnal and semidiurnal variation of rainfall over
Southeast China, Climate Dynamics, 39, 1913-1927 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-011-1236-5 (SCI) 62.
Gillies, R. R., S.-Y. Wang, and W.-R. Huang, 2012:
Observational and supportive modelling analyses of winter precipitation
change in China over the last half century. International Journal of
Climatology, 32: 747�V758. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.2303 (SCI) 63.
Huang, W.-R.*, S.-Y. Wang, and Johnny C. L. Chan, 2011:
Discrepancies between global reanalyses and
observations in the interdecadal variations of cold surge. International
Journal of Climatology, 31: 2272�V2280. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joc.2234 (SCI) 64.
Huang, W.-R*, and Johnny C. L. Chan, 2011: Maintenance
Mechanisms for the Early-Morning Maximum Summer Rainfall over Southeast
China. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 137:
959-968. DOI: 10.1002/qj.815https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/qj.815 (SCI) 65.
Wang, S. Y., R. E. Davies, W.-R. Huang, and R. R. Gillies, 2011: Pakistan's two-stage
monsoon and links with the recent climate change, J. Geophys. Res., 116, D16114. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2011JD015760 (SCI) 66.
Chen, T.-C., W.-R. Huang, and M.-C. Yen, 2011: Interannual Variation of the Late Spring-Early Summer Monsoon Rainfall
in the Northern Part of the South China Sea. J. Climate, 24, 4295-4313. https://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/full/10.1175/2011JCLI3930.1 (SCI) 67.
Yim, W. W.-S., W.-R. Huang, Chan, J. C. L., 2011: Climate
Change Corner: Hong Kong's Temperature Record. Hong Kong Engineer,
39(6), p 14. 68.
Huang, W.-R.*, Johnny C. L. Chan, and S.-Y. Wang, 2010:
A Planetary-scale Land-sea Breeze Circulation in East Asia and the Western
North Pacific. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 136: 1543�V1553. https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/qj.663 (SCI) 69.
Yim, W. W. -S., W.-R. Huang and J. C. L. Chan, 2010: Volcanoes and
Storms. Geoscientist, June issue, 20(6), 11-12. 70.
Chen, T.-C.*, S.-Y. Wang, W.-R. Huang, and M.-C. Yen,
2004: Variation of the East
Asian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. J.
Climate, 17, 744�V762. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0744:VOTEAS>2.0.CO;2 (SCI) 71.
Chen, T.-C.*, W.-R. Huang, and E.S. Takle, 2004: Annual
Variation of Midlatitude Precipitation. J. Climate, 17, 4291�V4298. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3201.1 (SCI) 72.
Chen, T.-C.*, W.-R. Huang, and J.h.
Yoon, 2004: Interannual
Variation of the East Asian Cold Surge Activity. J. Climate, 17, 401�V413. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0401:IVOTEA>2.0.CO;2 (SCI) 73.
Chen, T.-C.*, M.-C. Yen, W.-R. Huang, and W.-A. Gallus,
2002: An East Asian Cold Surge:
Case Study. Mon. Wea. Rev., 130,
2271�V2290. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2002)130<2271:AEACSC>2.0.CO;2 (SCI) Book Chapter Yoon, J.-H. and W.-R. (Judy) Huang (2012).
Indian Monsoon Depression: Climatology and Variability, Modern Climatology,
Shih-Yu (Simon) Wang and Robert R. Gillies (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0095-9, InTech pp45-72 2025May
Update |
|||