![]()
Air Pollution Modeling Environment (APoME) is a technology-enhanced learning environment that was designed to help high school students understand that air quality is the results of complex interactions among air pollutants, topographic effects, and meteorological variables. This learning environment (Air Pollution Modeling Environment, APoME) contains a computer-based modeling tool and five learning lessons.
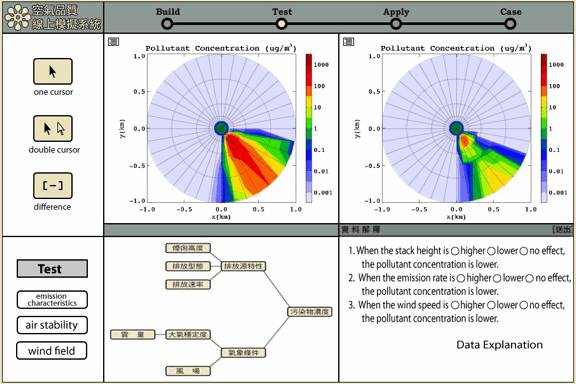
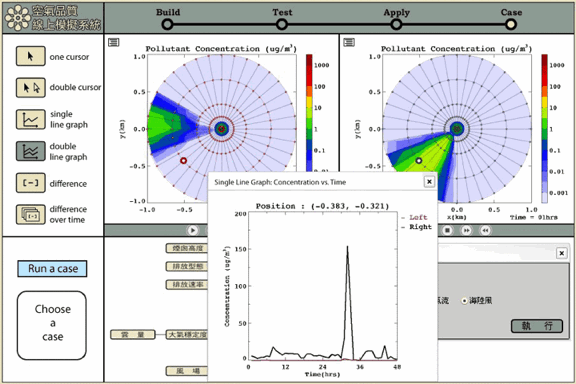
The modeling tool includes four modes: Build, Test, Apply, and Case. The Build mode allows students to identify variables that influence air pollutant dispersion and to establish relationships among variables. Students then could move to the Test mode to control and manipulate variables, use simulations to predict the concentration of air pollutant (SO2), and visualize the results. The Apply mode helps students manipulate multiple variables at the same time and visualize how the pollutant concentration changes within 48 hours. Specific cases are provided in the Case mode that support students to apply their models and concepts learned to explain different cases. The dispersion model behind all of the simulations is a professional model, AERMOD, that allows students to simulate the flow of air pollution in the atmosphere and to estimate the concentration of air pollutant.
The design of the five learning lessons followed the 5E's learning cycle (Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Extension, and Evaluation). These learning lessons take up fifteen 50-minute class periods and contain tool-based learning activities with the modeling tool. In the first lesson, teachers present news about air pollution and ask questions about air quality to stimulate students' thinking. Students then work in groups and engage in online searching to explore ideas such as PSI (Pollutant Standards Index), air quality reporting systems, and air quality testing. In the second and third lessons, teachers introduce variables that influence air pollutant dispersion such as atmospheric stability, wind speed, and topographic features. Student groups conduct hands-on experiments to make observations and explanations about diffusion phenomena. They are also encouraged to explore the relationships between the variables and the concentration of air pollutant and to use the relationships to explain why in some locations or under certain weather conditions, the air quality is getting better or worse. During the lessons four and five, students work with their group members and use the modeling tool to build a model about air pollutant dispersion. They are given two scenarios about air quality and asked to use their model to predict air quality in the scenarios. At the end of the fifth lesson, students evaluate the effectiveness of their model and identify the limitation of their model.
The implementation studies show that students' understandings about air quality were significantly improved after they engaged in the APoME activities. Students designed plans with detailed procedures, identified more major variables relevant to air pollutant dispersion, carefully controlled and manipulated variables to test their model, and provided multiple ways for data collection. These findings suggest that APoME is effective in supporting students to demonstrate expert-like modeling practices.
For more information, please contact us at hkwu@ntnu.edu.tw