spiral
spiral
「螺線」。繞圈的曲線。
radial function
X and F(X) ⇨ angle and radius
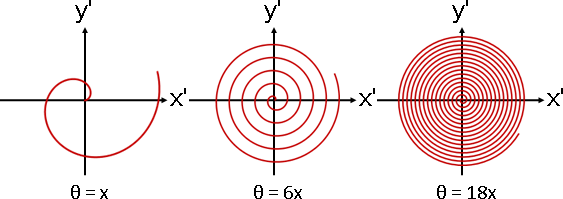
繪製函數圖形,除了水平延展,還可以迴旋延展。
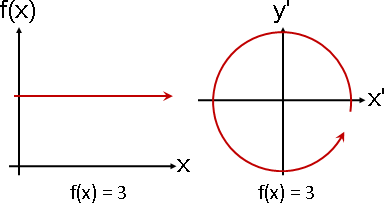
「徑向函數」。函數輸入視作從X軸出發的角度,函數輸出視作從原點出發的長度。
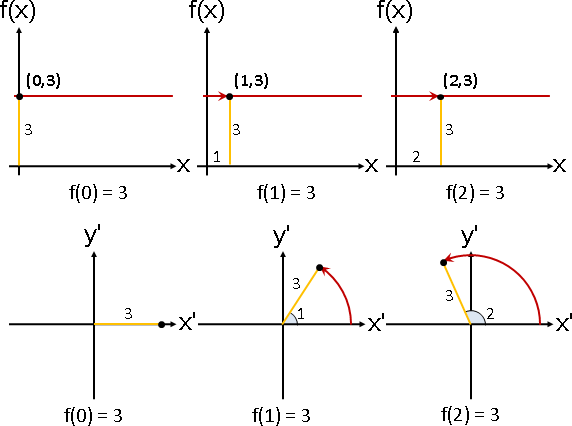
利用三角函數sin()和cos()找到繪製地點。
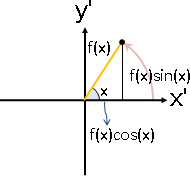
當函數輸出是負值,則無法畫出函數圖形。三種解法:一、乾脆不畫。二、負值變正值、換顏色。三、穿越原點,跑到對面,角度相差180度。
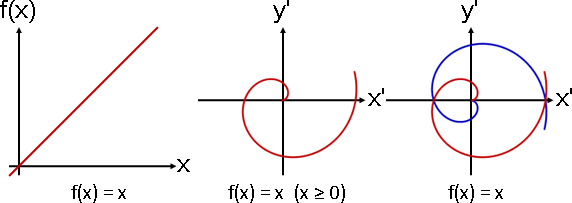
角度可以改成x的倍率,修改轉速。
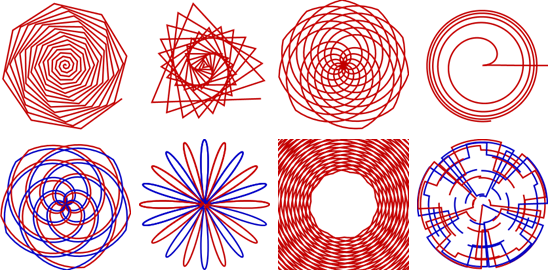
運用迴旋,得以製作許多特殊圖形。
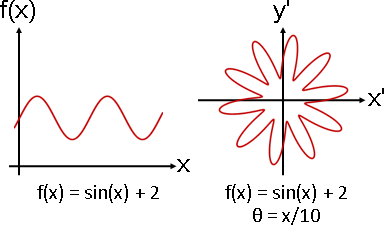
periodicity ⇨ closed
有個值得一提的案例是週期函數:固定間距、不斷重複的函數。
角度改成x的適當倍率,使得一個間距(或者其倍數)剛好轉一圈,函數圖形頭尾銜接,得到封閉曲線。
angle and radius ⇨ X and F(X)【查無專有名詞】
任意的封閉曲線,想要從迴旋延展變成水平延展,就必須滿足函數的規定:找到內部一點作為原點,任意放射線與曲線的交點只有一點。之後即可視作一般函數進行處理。
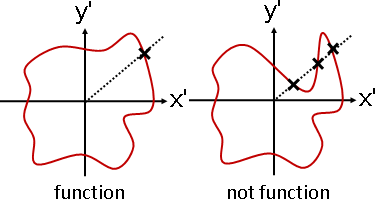
不是函數的封閉曲線,想要滿足函數的規定,我只知道一種解法是平滑化:每一個點,取其鄰點,求平均數。實施足夠次數,似乎就會變成函數。實施無限次,最後就會變成圓形,其概念類似於流形與圓的映射。我不清楚這部分是否有人研究。
sphere coordinates、函數輸入是兩個變數
函數輸入是兩個變數(或者一個複數),視作旋轉角度和俯仰角度,得到三維空間的表面。
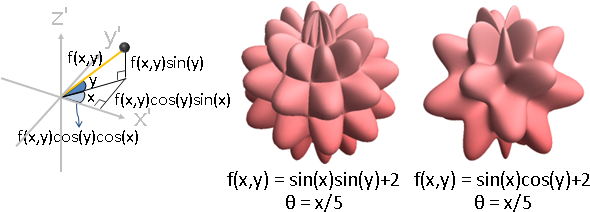
f[u_,v_] := Sin[u]Sin[v]+2; ParametricPlot3D[{f[u,v]Cos[v/5]Cos[u/5], f[u,v]Cos[v/5]Sin[u/5], f[u,v]Sin[v/5]}, {u, 0, 40}, {v, 0, 40}, Boxed -> False, Axes -> False, Mesh -> None, PlotPoints -> 70, ColorFunction -> (ColorData["CherryTones"][Rescale[#3, {-2, 2}]] &) ]
cylinder coordinates、函數輸出是兩個變數
函數輸出是兩個變數(或者一個複數),視作水平距離和垂直距離,得到三維空間的線。
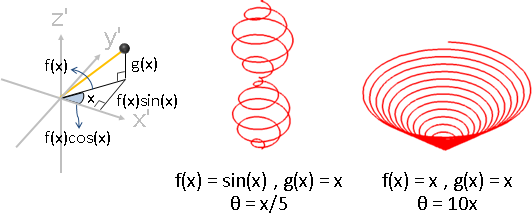
ParametricPlot3D[{Sin[x] Cos[x*10], Sin[x] Sin[x*10], x}, {x, 0, 9}, Boxed -> False, Axes -> False, PlotStyle -> {RGBColor[192,0,0], Thick}]